DNS Server
- Authors
- Name
- Michael Bui
Overview
Documentation: Microsoft Docs
DNS Server provides name resolution to computers and users by mapping computer names to IP addresses. DNS allows us to use friendly names that can be easily remembered instead of IP addresses.
In Windows Server, DNS is a server role that you can install. However, in this lab we already have the DNS role installed because we installed AD DS on the server previously.
In this lab, we'll be configuring the DNS Server role on SVR01 to allow name resolution for the PCs in our domain.
Instructions
Forward Lookup Zones
Forward lookup zones let us map host names to IP addresses
- Open DNS manager
- Right click Forward Lookup Zone -> New Zone
- Choose replication settings
- Configure Dynamic Update - This allows hosts to add A records to the forward lookup zone when they are part of the domain
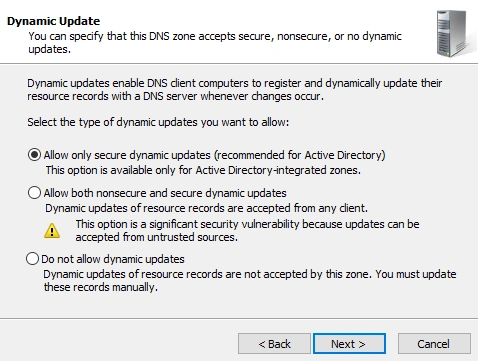
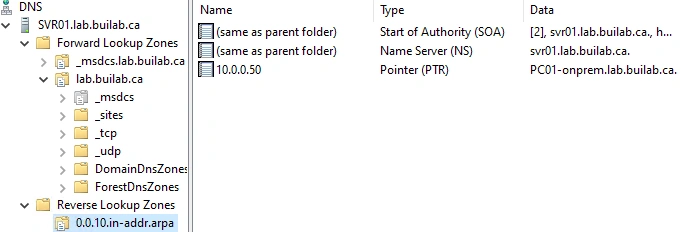
- We can see that
PC01added it's A record dynamically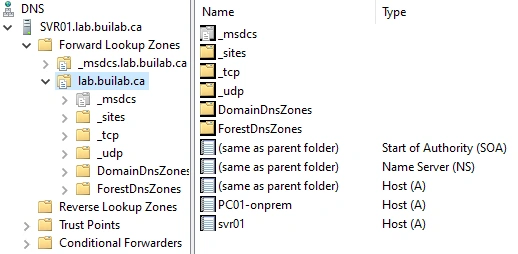
Reverse Lookup Zones
Reverse lookup zones let us find the host name of an IP address
- Right click Reverse Lookup Zone -> New Zone
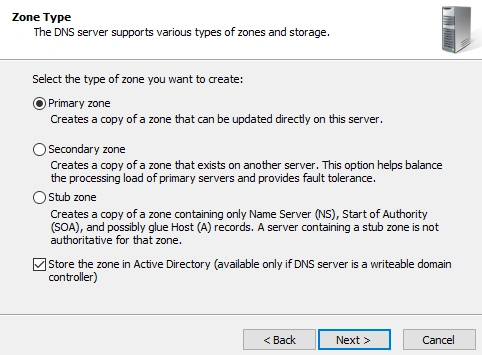
- Create a new Primary Zone
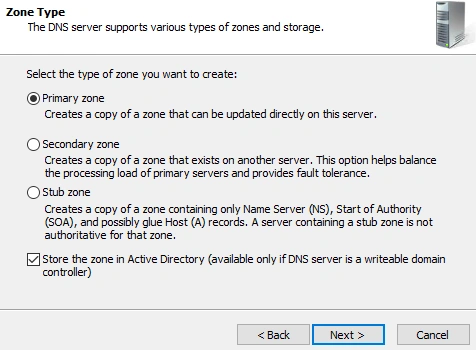
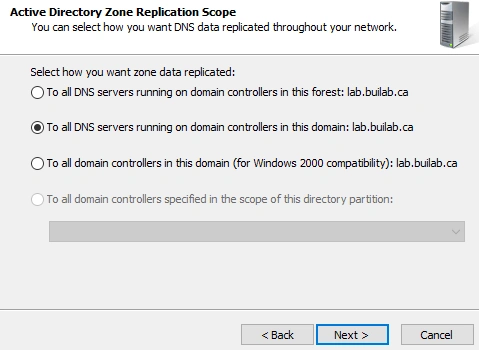
- Configure Replication
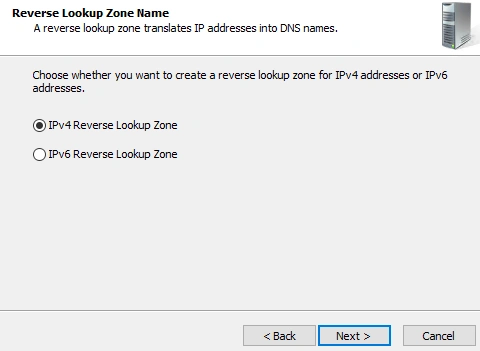
- Choose type of reverse lookup. We're going to work with IPv4
- Set the network portion of the IP space for the network. The network portion of our IP space is
10.0.0we're using a subnet mask of255.255.255.0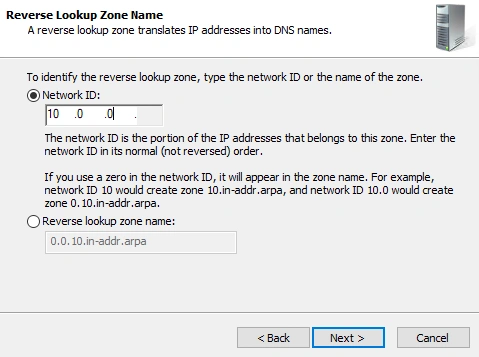
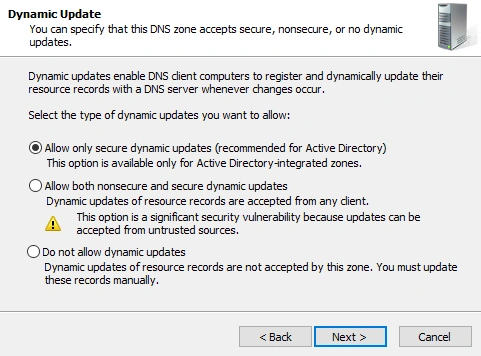
- Allow records to by dynamically added
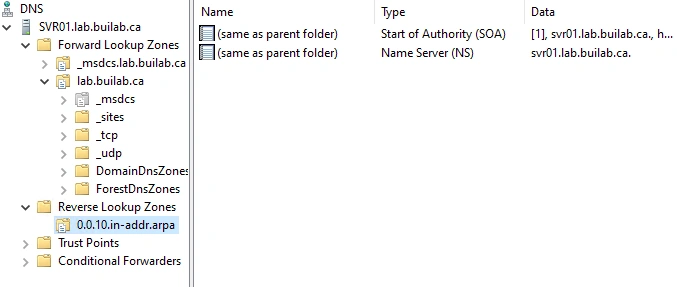
- Our reverse lookup zone configuration is completed
Results
- On
PC01, I pingedSVR01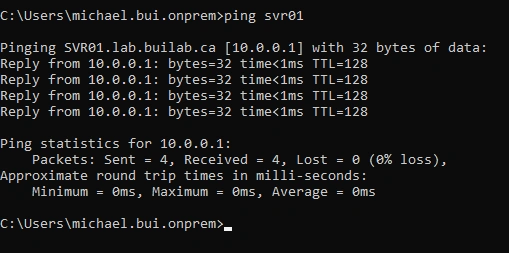
SVR01is the host name and DNS points it to thelab.builab.cadomain- If we ping a host name that doesn't exist like
SVR02DNS will not be able to resolve the name
- We can add an A record for
SVR02and DNS will be able to resolve it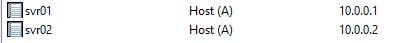
- Pinging
SVR02again, the name resolves to our A record of10.0.0.2, however I do not haveSVR02online so the ping request fails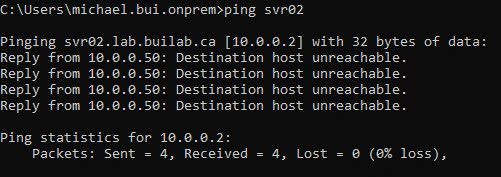
- The IP address of PC01 is known to the DNS server via DHCP assignment and a PTR record is dynamically created in the Reverse lookup zone